What is Caching? A Simple Guide for Product Managers
Learn how caching boosts performance, saves resources, and enhances user experience.
What’s a Cache?
In the world of computing, the term "cache" frequently surfaces, particularly when discussing performance optimization. But what exactly is a cache, and why is it so critical for modern applications and systems? Let’s dive into the basics of caching, its importance, and the various types of caches.
Basics of Caching
At its core, a cache is a high-speed data storage layer designed to store frequently accessed data temporarily. By keeping this data closer to where it is needed, caching reduces the time and resources required to retrieve it. Think of it as a shortcut: instead of fetching data from a slow or distant source, a system can pull it directly from the cache, resulting in much faster responses.
For example, imagine you’re visiting a website. The first time you load it, your browser fetches data like images, scripts, and stylesheets from the server. On subsequent visits, instead of downloading these files again, your browser retrieves them from its local cache, speeding up the page load time.
The Role of Caching in Performance Optimization
Caching plays a pivotal role in improving the performance of applications and systems. Here’s how:
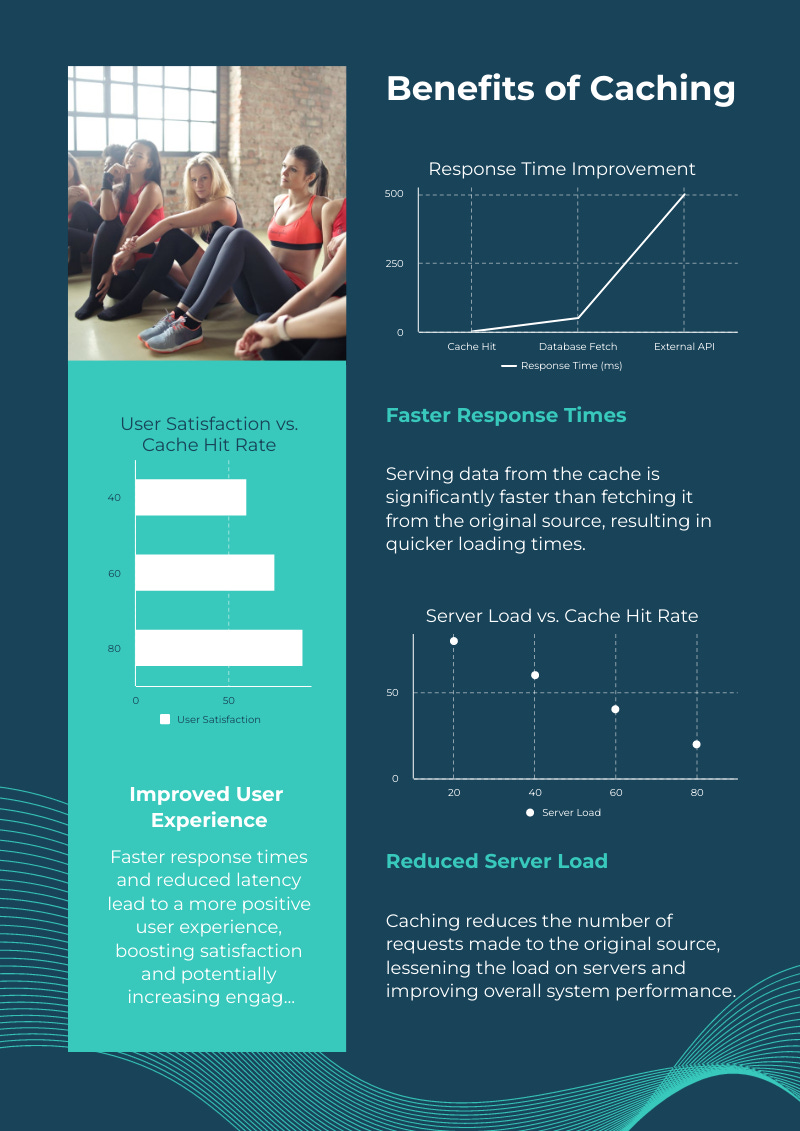
Reduced Latency: Accessing data from a cache is significantly faster than fetching it from the original source.
Lower Network Load: By serving cached content, systems reduce the amount of data that needs to travel across networks.
Decreased Server Load: Caching reduces the frequency of requests hitting the server, allowing it to handle more users simultaneously.
Improved User Experience: Faster response times translate to smoother, more satisfying user interactions.
Types of Caches
Caches exist at different layers of the technology stack. Here are the two most common types:
Browser Cache:
This type of cache is managed by web browsers. When you visit a website, the browser stores resources like HTML, CSS, JavaScript files, and images locally on your device.
On subsequent visits to the same site, the browser checks if it can serve content from its cache instead of downloading it again.
This not only speeds up page load times but also reduces bandwidth usage.
Server Cache:
A server cache stores data closer to the backend system, often in memory or a dedicated caching layer.
Examples include database query results, pre-rendered HTML pages, or API responses.
Common server caching systems include Redis, Memcached, and Varnish.
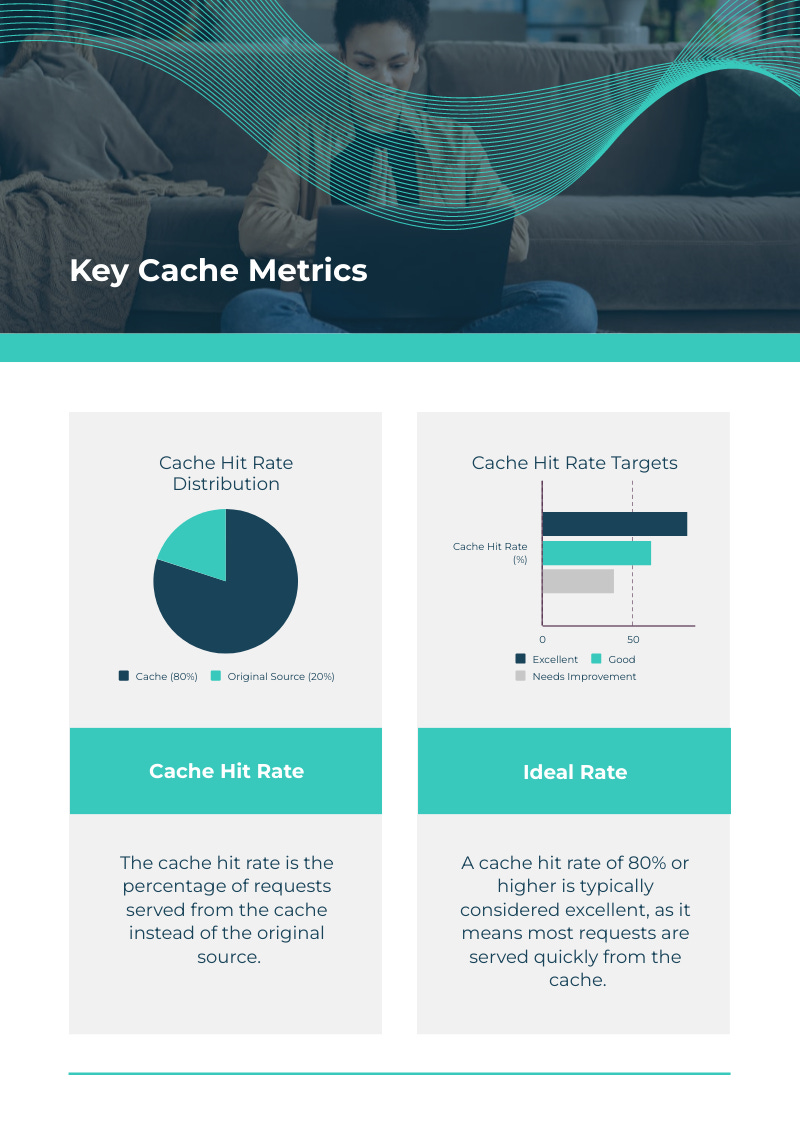
Server caching is particularly useful for high-traffic websites and applications, where reducing load on the database or backend can dramatically improve performance.
Use Cases of Caches for PMs
Product Managers (PMs) should understand several practical use cases of caches:
Web Page Speed Optimization:
Caching assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript on the browser ensures faster load times for users revisiting a website.
Metrics: Studies show that reducing page load time from 8 to 2 seconds can increase conversion rates by up to 74%.
API Response Optimization:
Database Query Optimization:
Complex database queries can be cached to prevent repetitive computations, significantly improving application performance.
Example: Using Redis to cache product search results in an e-commerce application.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
CDNs like Cloudflare and Akamai use caching to store website assets on servers distributed globally, reducing latency for users accessing the site from various locations.
Session Management:
Caching user session data ensures that applications can retrieve session details quickly without querying the database repeatedly.
Popular Caching Solutions
Here are some widely-used caching tools and systems:
Redis: Known for its speed and flexibility, Redis is a popular choice for caching and real-time data processing.
Memcached: A lightweight caching solution ideal for simple use cases.
Varnish Cache: Used primarily for HTTP caching, making it perfect for web applications.
Conclusion
Caching is a cornerstone of efficient computing. By storing frequently accessed data in a high-speed storage layer, it helps minimize delays, reduce resource usage, and enhance the overall experience for users. Whether it’s your browser saving images locally or a server optimizing database calls, caching ensures that modern systems perform at their best.
For more information, check out these resources: